本文介绍路径点的优化方式,或者叫做多线段优化、轨迹点优化
根据设定阈值,去掉路径点中的部分多余点,以达到方便传输的目的
本文用UE4蓝图和C++蓝图函数库的2个方式解释
注:多种方法可以叠加使用
本算法提供了基于UE4的Demo,PC,安卓
GitHub工程下载
Demo演示动图

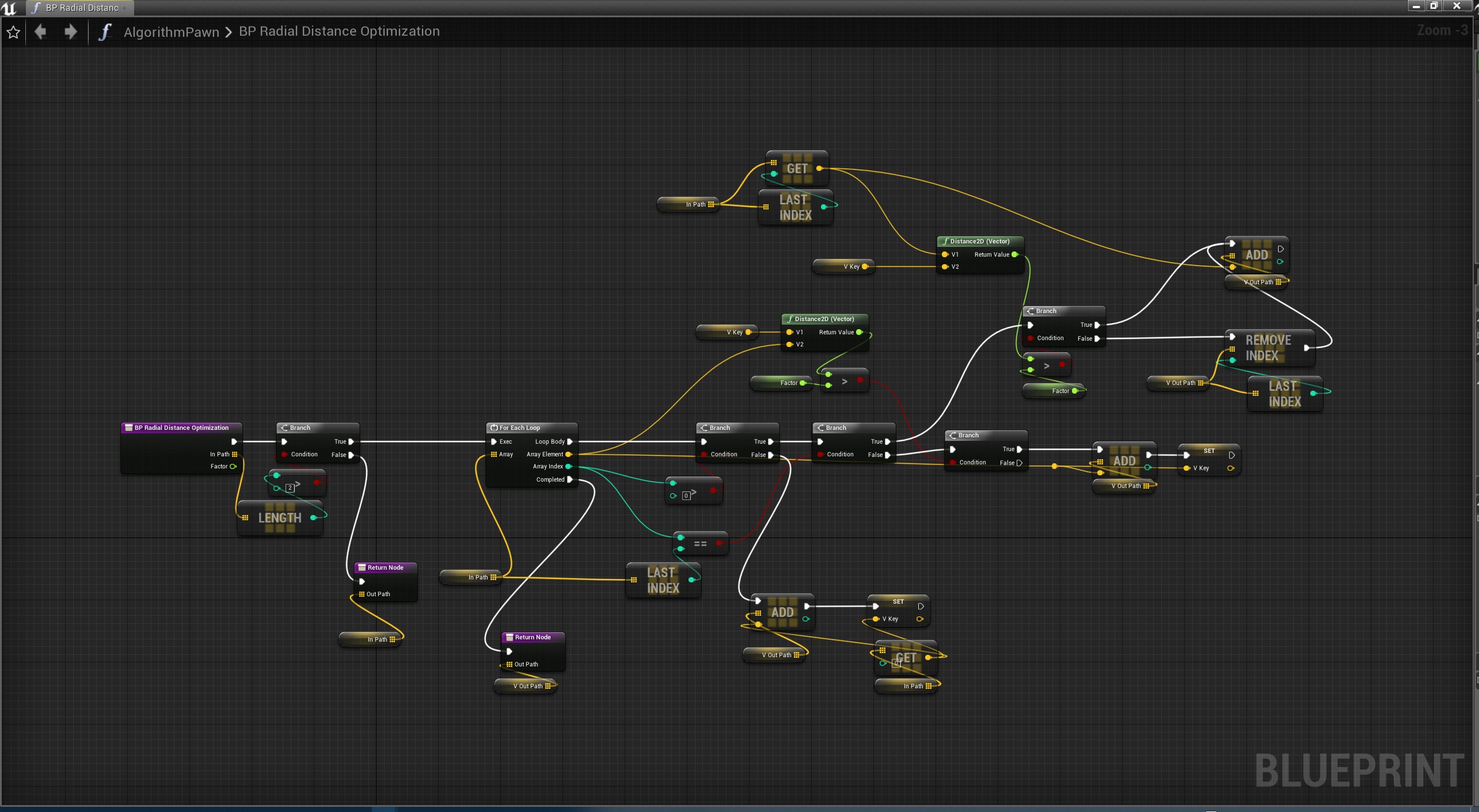
径向距离算法
又称为临近点优化,比较暴力的算法,效率高,精准度尚可
目的:去掉太接近的点
如果路径点中的相邻两点的距离小于设定的阈值,则舍去其中一个点。首先,以笔迹中的第一个点为基准点,计算第二个点与第一个点之间的距离,如果此距离小于给定的阈值,则舍去第二个点;如果此距离大于给定的阈值,则保留第二个点,并以其为新的基准点。然后再拿第三个点来与基准点判断距离,如此向后循环。
先贴代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable,Category="UFlibAlgorithm|PathPointOptimization")
static bool RadialDistanceOptimization(const TArray<FVector>& InPath,TArray<FVector>& OutPath, float Distance=50);
bool UFlibAlgorithm::RadialDistanceOptimization(const TArray<FVector>& InPath, TArray<FVector>& OutPath, float Distance)
{
if (InPath.Num()<3)
{
OutPath = InPath;
return false;
}
FVector vKey= InPath[0];
OutPath.Add(vKey);
for (int32 i=1;i< InPath.Num()-1;i++)
{
if ((vKey- InPath[i]).Size()> Distance)
{
OutPath.Add(InPath[i]);
vKey = InPath[i];
}
}
if ((InPath.Last()-vKey).Size()<=Distance)
{
OutPath.Pop();
}
OutPath.Add(InPath.Last());
return true;
}
|
蓝图
曲率算法
去除大于设定曲率阈值的角度的点
目的:去除角度偏移过大的线段
设定3个点:p1,p2,p3
方向向量:前置向量v1=p2-p1,后置向量v2=p3-p2
v1和v2的夹角angle即我们需要与阈值比较的角度,如果大于阈值,那么点p2就不满足条件而被移除
这里带来了一个问题,即移除了p2以后,下一次计算的时候后置向量v2保持不变即当前点指向下一个点;但是前置向量怎么选择是一个问题,所以我们分别用了T124,T134,T234来分别3种计算方式,3种方式取前置向量的方式分别是
- T124:前置向量v1=p2-p1,即保持原样
- T134:v1=p3-p1,即跳过被移除点
- T234:v1=p3-p2,即跟后置向量保持统一节奏
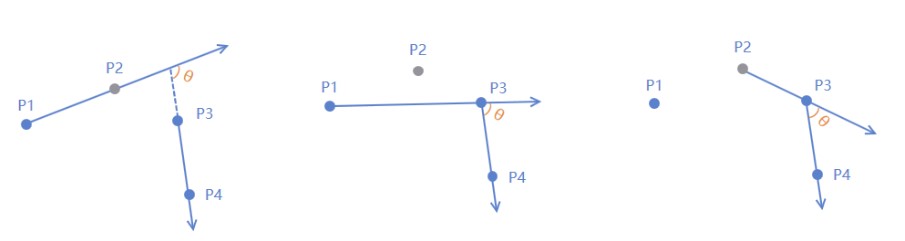
三种方式计算方式大同小异,下面先贴代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
UENUM(BlueprintType)
enum class ECurvatureType:uint8
{
T124,
T134,
T234
};
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "UFlibAlgorithm|PathPointOptimization")
static bool CurvatureOptimization(const TArray<FVector>& InPath, TArray<FVector>& OutPath, ECurvatureType type=ECurvatureType::T134, float Angle = 90);
bool UFlibAlgorithm::CurvatureOptimization(const TArray<FVector>& InPath, TArray<FVector>& OutPath, ECurvatureType type, float Angle )
{
if (InPath.Num() < 3)
{
OutPath = InPath;
return false;
}
FVector p1 = InPath[0];
OutPath.Add(p1);
FVector p2, p3, dirFWD, dirBWD;
bool b124Found = true;
for (int32 i=1;i<InPath.Num()-1;i++)
{
p2 = InPath[i];
p3 = InPath[i + 1];
if (b124Found||type!=ECurvatureType::T124)
{
dirFWD = p2 - p1;
}
dirBWD = p3 - p2;
if (AngleBetween(dirBWD, dirFWD) <= Angle)
{
OutPath.Add(p2);
p1 = p2;
b124Found = true;
}
else
{
b124Found = false;
if (type==ECurvatureType::T234)
{
p1 = p2;
}
}
}
OutPath.Add(InPath.Last());
return true;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| float UFlibAlgorithm::AngleBetween(FVector A, FVector B)
{
A.Normalize();
B.Normalize();
return UKismetMathLibrary::DegAcos(UKismetMathLibrary::Dot_VectorVector(A, B));
}
|
蓝图
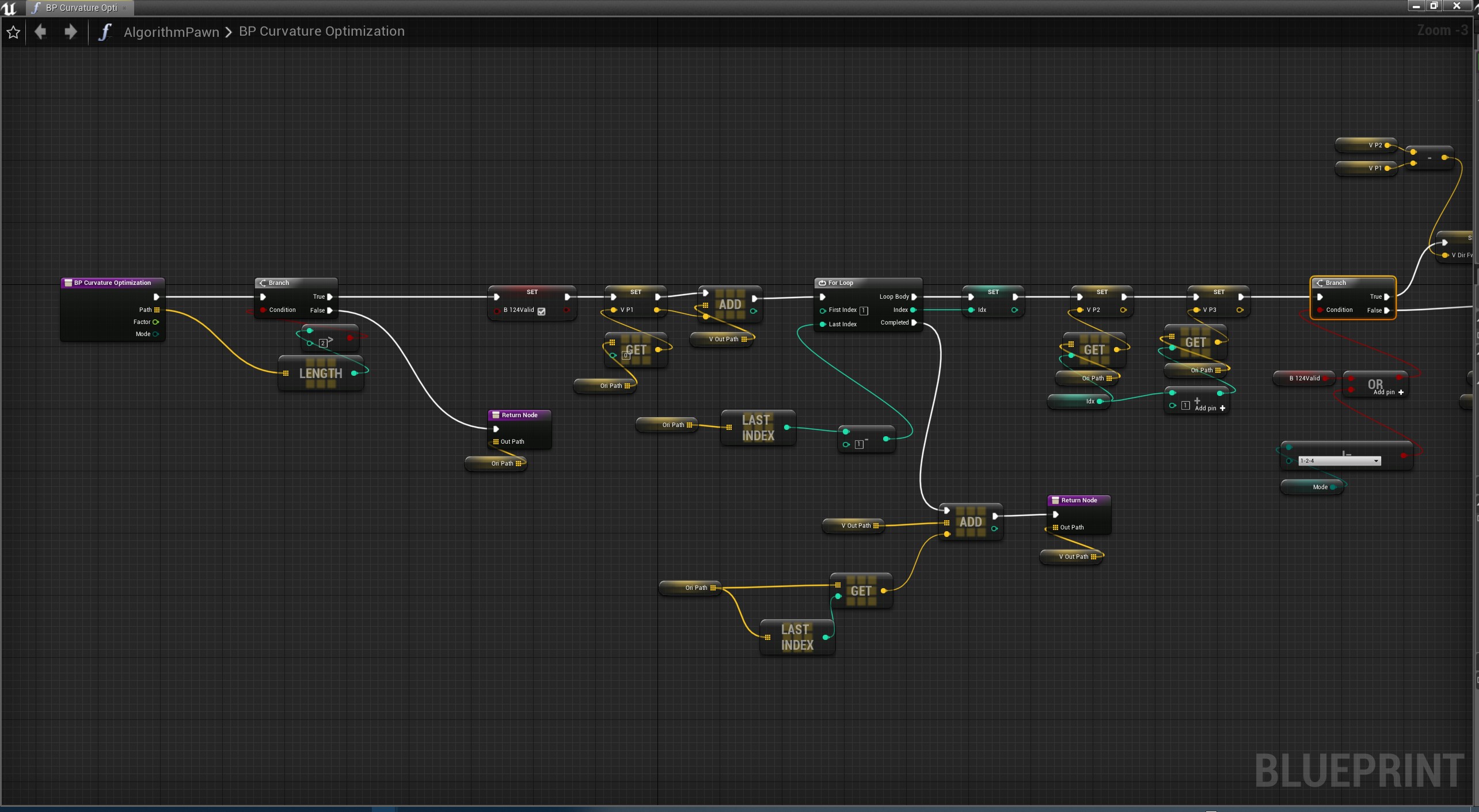
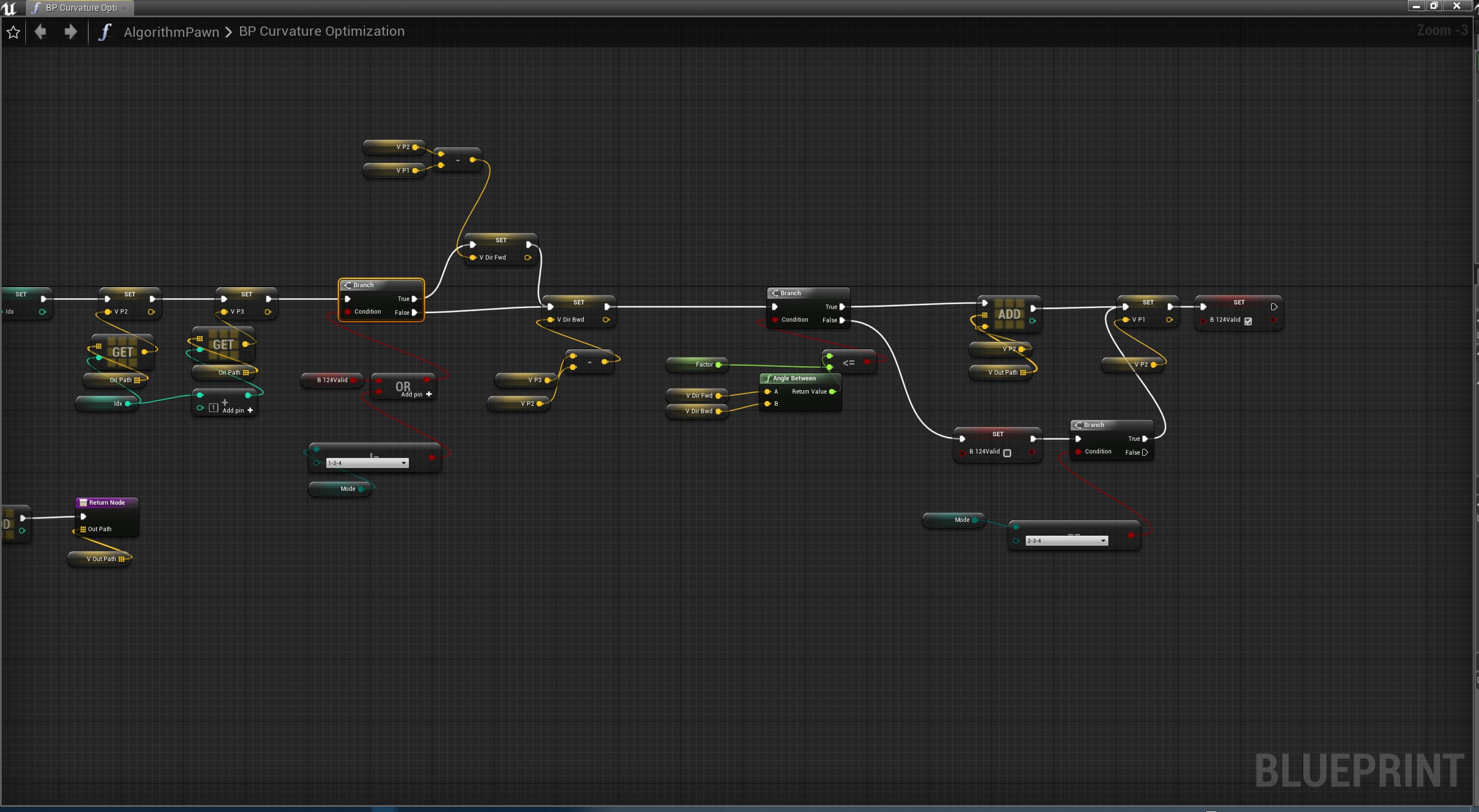
从结果测试发现,效果 T134>T124>T234
垂直距离算法
将点-线段的距离作为误差判据。对于每个顶点p,需要计算它与线段[p-1, p+1]的垂直距离,距离比给定误差小的点都将被移除。
目的:去除垂直距离偏移过大的点
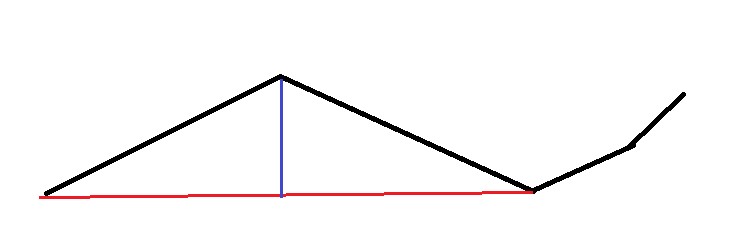
如图,如果蓝色线段即垂直距离大于设定阈值,则左右两天线段会被优化成红色线段
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "UFlibAlgorithm|PathPointOptimization")
static bool PerpendicularDistanceOptimization(const TArray<FVector>& InPath, TArray<FVector>& OutPath, float Distance = 50);
bool UFlibAlgorithm::PerpendicularDistanceOptimization(const TArray<FVector>& InPath, TArray<FVector>& OutPath, float Distance )
{
if (InPath.Num() < 3)
{
OutPath = InPath;
return false;
}
FVector vKey = InPath[0];
OutPath.Add(vKey);
FVector p1, p2, p3;
p1 = InPath[0];
for (int32 i=1;i<InPath.Num()-1;i++)
{
p2 = InPath[i];
p3 = InPath[i + 1];
float dis = UKismetMathLibrary::GetPointDistanceToLine(p2, p1, p3 - p1);
if (dis<=Distance)
{
OutPath.Add(p2);
p1 = p2;
}
}
OutPath.Add(InPath.Last());
return true;
}
|
蓝图
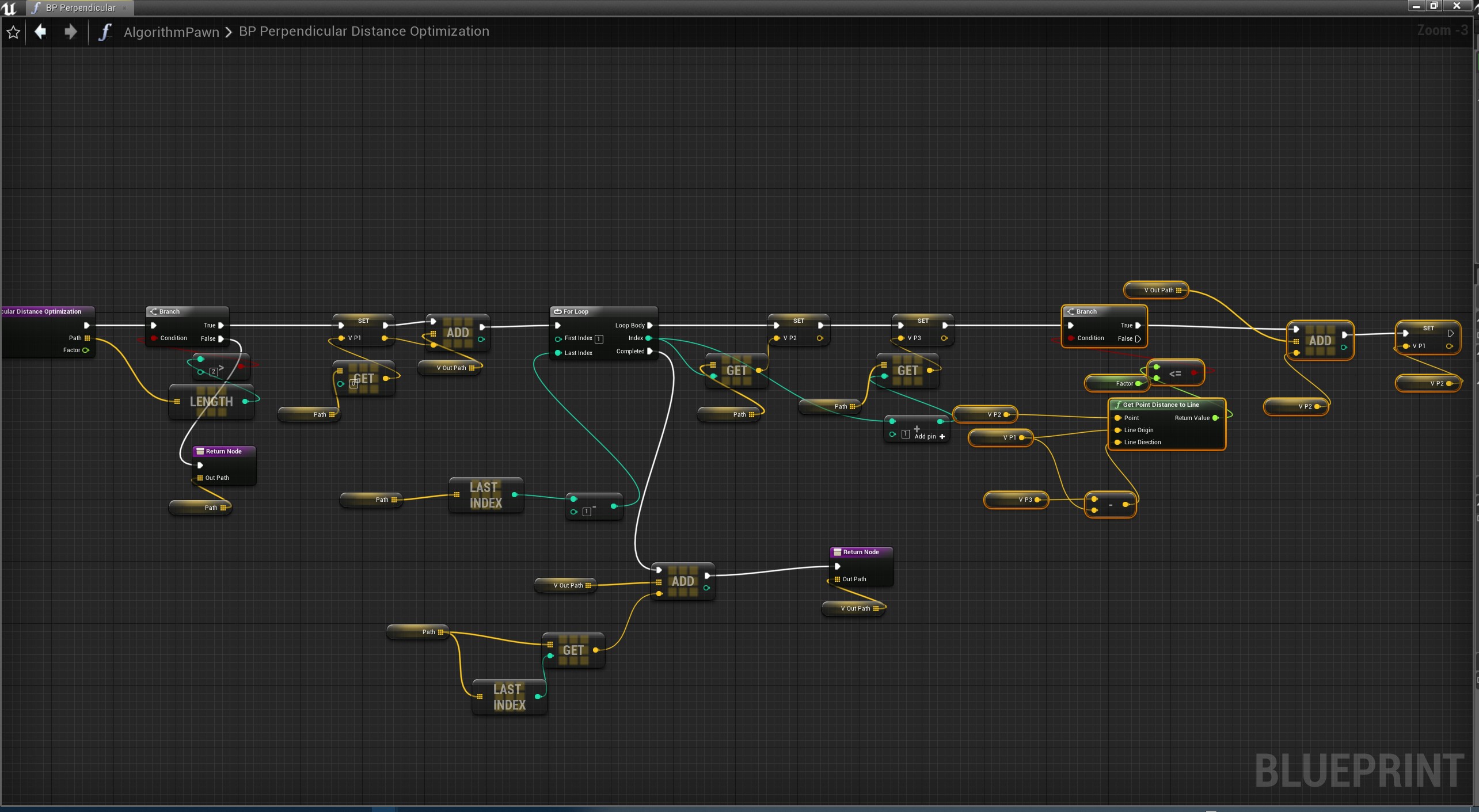
其实参考曲率优化方式,这个方式也可以考虑3种前置向量即本代码中p1的选择问题,本代码种应该是类似T234的方式,有兴趣的可以自己尝试其他几个方式
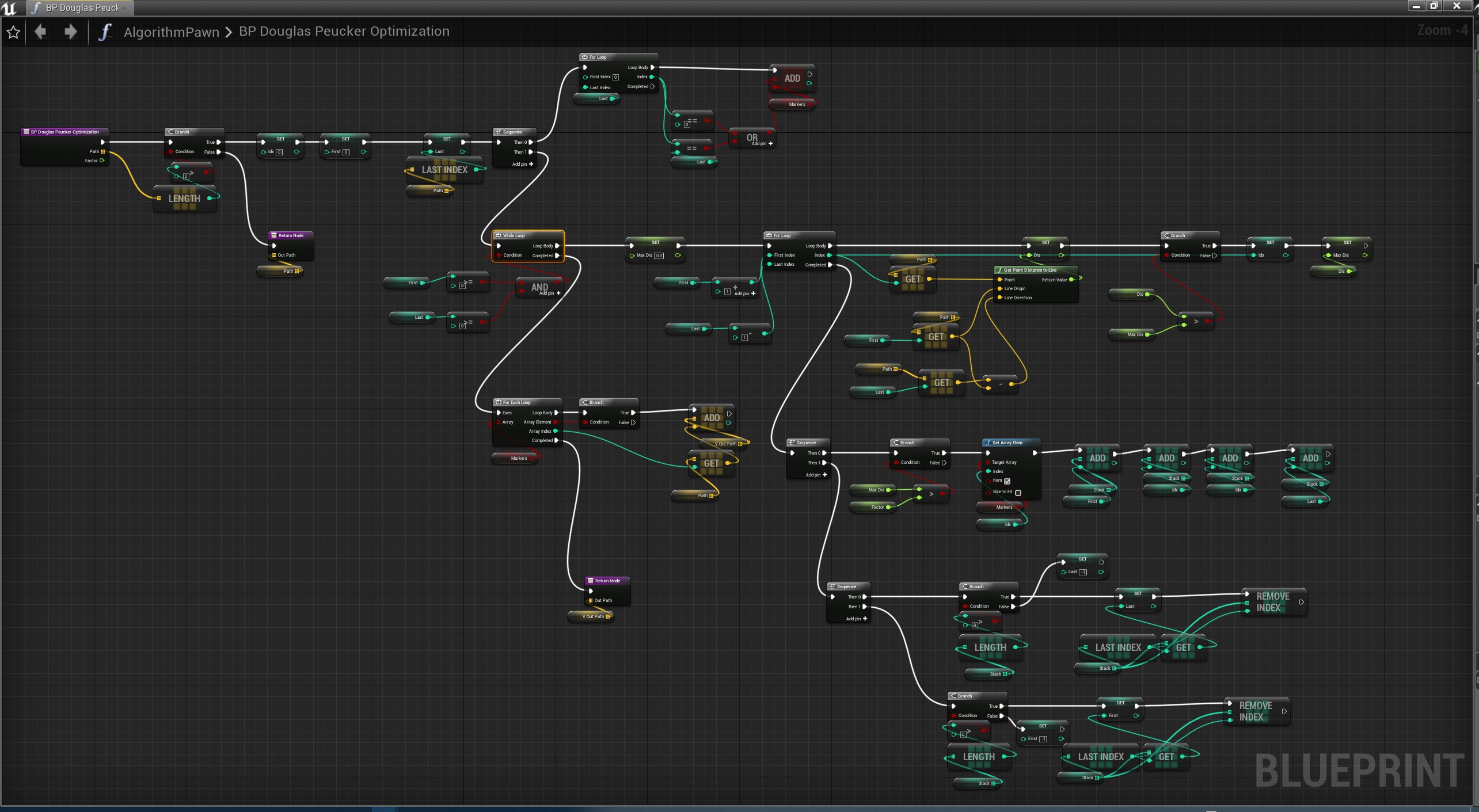
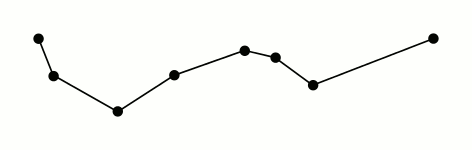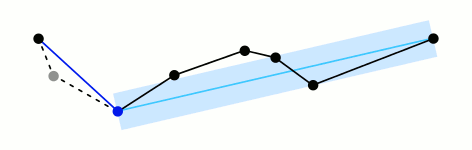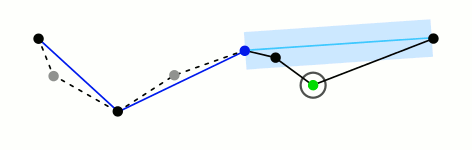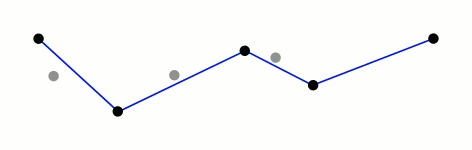
道格拉斯-普克算法
一种迭代适应点算法,它将曲线近似表示为一系列点,并减少点的数量。
算法的基本思路是:对每一条曲线的首末点虚连一条直线,求所有点与直线的距离,并找出最大距离值 dmax ,用 dmax 与阈值 D 相比。若 dmax < D ,这条曲线上的中间点全部舍去;若 dmax ≥ D ,则保留 dmax 对应的坐标点,并以该点为界,把曲线分为两部分,对这两部分循环使用该方法。
此算法在时间复杂度和空间复杂度要明显高于其它两种,但是它的效果较好
先来一个动图
贴代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
|
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "UFlibAlgorithm|PathPointOptimization")
static bool DouglasPeuckerOptimization(const TArray<FVector>& InPath, TArray<FVector>& OutPath, float Distance = 50);
bool UFlibAlgorithm::DouglasPeuckerOptimization(const TArray<FVector>& InPath, TArray<FVector>& OutPath, float Distance )
{
if (InPath.Num() < 3)
{
OutPath = InPath;
return false;
}
int32 idx, first, last;
first = idx = 0;
last = InPath.Num() - 1;
TArray<bool> Markers;
Markers.AddUninitialized(last + 1);
Markers[0] = true;
Markers.Last() = true;
float maxDis = 0;
TArray<int32> stack;
while (first>=0 && last>=0)
{
maxDis = 0;
for (int32 i=first+1;i<last;i++)
{
float dis = UKismetMathLibrary::GetPointDistanceToLine(InPath[i], InPath[first], InPath[last] - InPath[first]);
if (dis>maxDis)
{
idx = i;
maxDis = dis;
}
}
if (maxDis>Distance)
{
Markers[idx] = true;
stack.Add(first);
stack.Add(idx);
stack.Add(idx);
stack.Add(last);
}
if (stack.Num()>0)
{
last = stack.Pop();
}
else
{
last = -1;
}
if (stack.Num() > 0)
{
first = stack.Pop();
}
else
{
first = -1;
}
}
for (int32 i=0;i<Markers.Num();i++)
{
if (Markers[i])
{
OutPath.Add(InPath[i]);
}
}
return true;
}
|
蓝图